Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
The fashion industry is undergoing a transformative shift as the rise of virtual fashion design reshapes how garments are conceptualized, created, and showcased. For fashion designers and buyers involved in bulk garment fabrication, understanding the behind-the-scenes processes of virtual fashion design is essential to harnessing its full potential. This blog post will take you on a journey through the intricate steps involved in virtual fashion design, offering insights into the tools, techniques, and creativity that drive this innovative approach.
Why Virtual Fashion Design Matters
Virtual fashion design is not just a trend; it’s a game-changer in the industry. Here’s why it matters:
- Efficiency: Digital tools streamline the design process, reducing the time and resources needed to create and modify garments.
- Sustainability: By minimizing the need for physical samples, virtual fashion design significantly reduces waste and the environmental impact of the fashion industry.
- Creativity Unleashed: Designers can experiment with limitless possibilities, from fabric textures to intricate patterns, without the constraints of physical materials.
- Global Collaboration: Virtual design enables seamless collaboration between teams across the world, making it easier to work with international partners and clients.
Step 1: Conceptualizing the Design
The first step in virtual fashion design is the conceptualization phase, where the designer's vision takes shape.
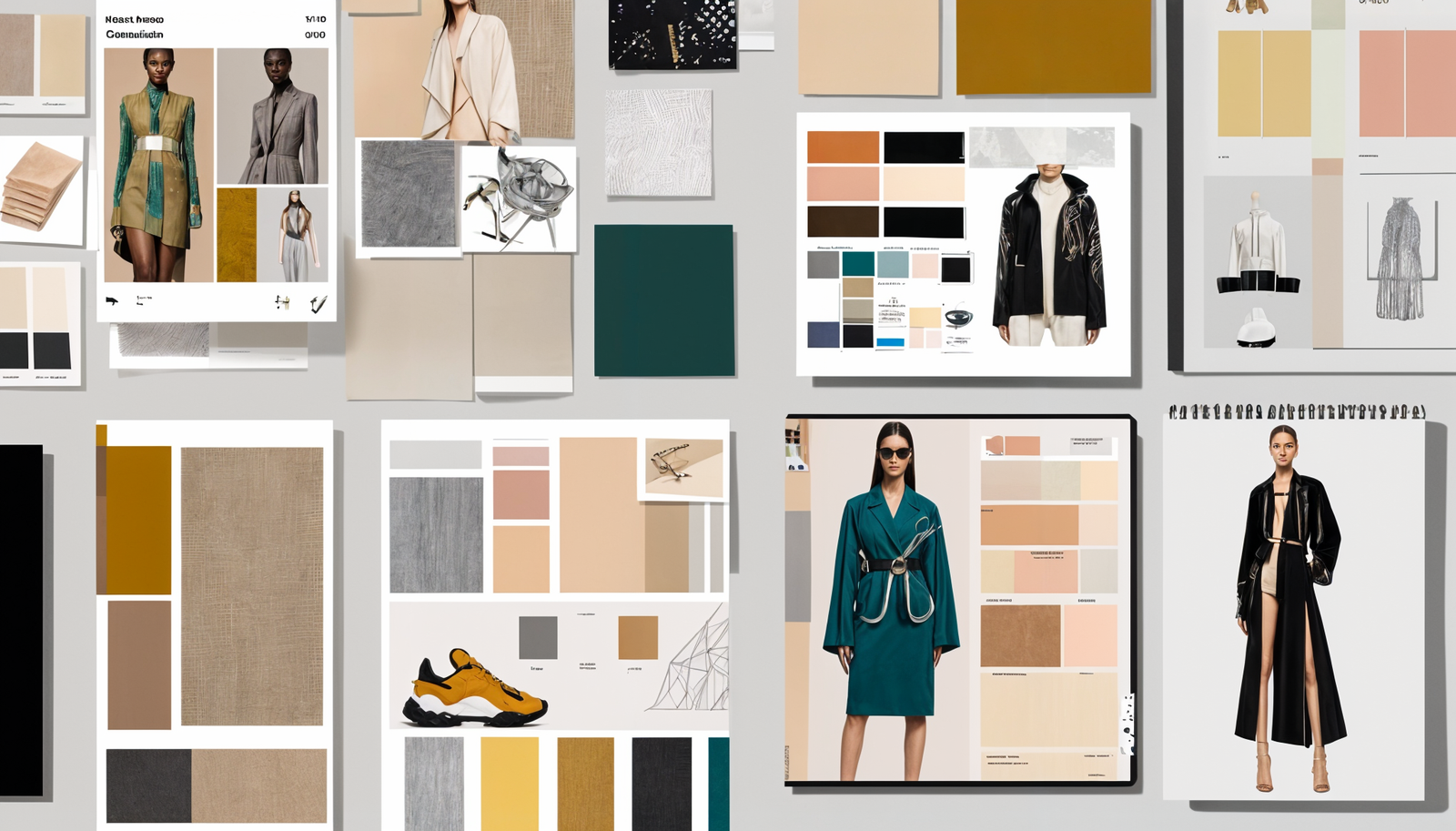
1.1 Inspiration and Mood Boards
Designers start by gathering inspiration, often creating digital mood boards to organize their ideas. These boards include images, color palettes, and textures that reflect the desired aesthetic.
- Tools: Popular tools for creating digital mood boards include Pinterest, Adobe Spark, and Milanote.
- Themes: The theme can range from seasonal inspirations to futuristic concepts, depending on the designer's vision.
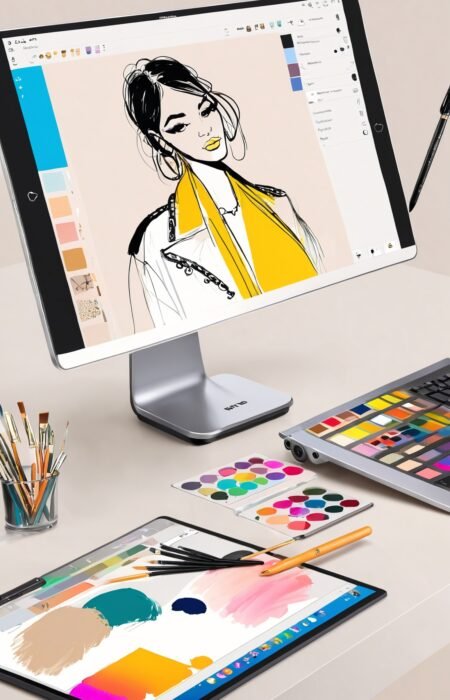
1.2 Sketching and Illustration
Once the concept is clear, designers move on to sketching their ideas. In virtual fashion design, this step often involves digital illustration tools that allow for more flexibility and precision.
- Software: Tools like Adobe Illustrator, Procreate, and CorelDRAW are widely used for digital sketching.
- Digital Brushes: These tools offer various digital brushes that mimic traditional art supplies, allowing designers to create detailed and nuanced sketches.
Step 2: 3D Modeling and Garment Construction
After the initial design phase, the next step is to bring the sketches to life through 3D modeling and garment construction.
2.1 Creating 3D Models
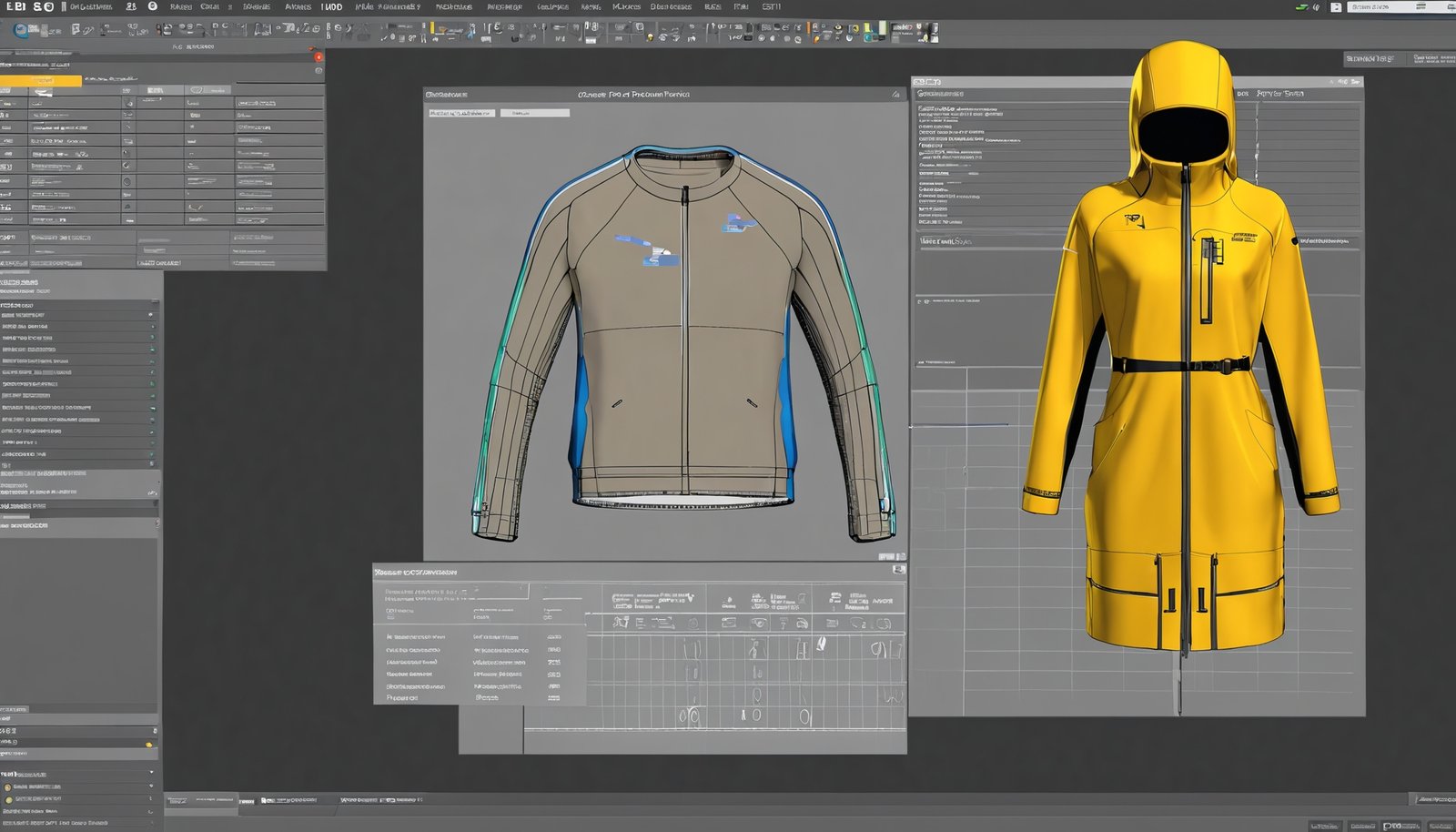
The heart of virtual fashion design lies in 3D modeling. Designers use advanced software to create realistic 3D models of their garments.
- Software: CLO 3D, Marvelous Designer, and Blender are some of the most popular tools for 3D garment modeling.
- Precision: These tools allow designers to adjust every detail, from fabric drape to seam placement, ensuring that the digital garment looks and behaves like a real one.
2.2 Fabric Simulation
One of the most impressive aspects of virtual fashion design is fabric simulation, where digital fabrics are created to mimic the properties of real-world textiles.
- Textures and Materials: Designers can choose from a wide range of textures and materials, such as silk, wool, and denim, to simulate the look and feel of the fabric.
- Physics Engines: The software uses physics engines to replicate how the fabric moves, folds, and interacts with the virtual model.
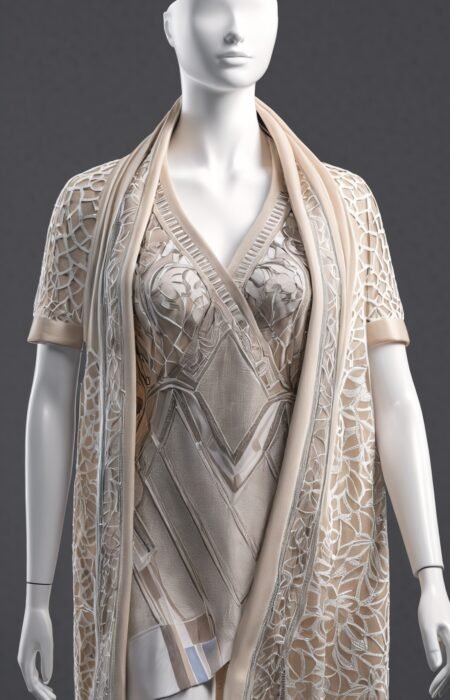
2.3 Virtual Draping
Virtual draping allows designers to see how their garments will look on a digital model, enabling them to make adjustments before any physical production begins.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Designers can make real-time adjustments to the fit, silhouette, and details of the garment.
- Customization: The virtual model can be customized to reflect different body types, ensuring that the garment looks perfect on all potential customers.
Step 3: Rendering and Visualization
Once the garment is constructed, the next step is rendering and visualization, where the design is brought to life in a virtual environment.
3.1 High-Quality Rendering
Rendering is the process of generating high-quality images of the 3D garment. This step is crucial for visualizing the final product and creating marketing materials.
- Rendering Software: Tools like KeyShot, V-Ray, and Arnold are commonly used for rendering in fashion design.
- Lighting and Shadows: Designers can manipulate lighting and shadows to create realistic effects that enhance the appearance of the garment.
3.2 Virtual Runway and Lookbook Creation
With the rendered images, designers can create virtual lookbooks or stage a virtual runway show to showcase their collection.
- Lookbooks: Digital lookbooks can be shared with buyers and clients, providing a comprehensive view of the collection.
- Virtual Runways: Designers can create a virtual runway experience, complete with animated models and dynamic backgrounds.
Step 4: Collaborative Design and Feedback
Collaboration is a key component of the virtual fashion design process, allowing designers to work with teams and clients around the world.
4.1 Cloud-Based Design Platforms
Cloud-based platforms facilitate real-time collaboration, enabling designers, manufacturers, and clients to work together seamlessly.
- Tools: Platforms like Adobe Creative Cloud, Figma, and ZBrushCore allow for shared access to design files and real-time feedback.
- Version Control: These platforms offer version control, ensuring that all team members are working with the latest version of the design.
4.2 Client Feedback and Revisions
Virtual design allows for easy revisions based on client feedback, reducing the time and cost associated with physical samples.
- Interactive Prototypes: Designers can create interactive prototypes that clients can view and manipulate, providing a more immersive experience.
- Instant Updates: Changes can be made instantly, with updated designs available for review in real-time.
Step 5: Preparing for Production
The final step in the virtual fashion design process is preparing the garment for production. This step involves creating detailed technical specifications and ensuring that the design is ready for manufacturing.
5.1 Technical Packs
Technical packs, or tech packs, are detailed documents that outline every aspect of the garment’s design and construction.
- Components: A tech pack includes information on materials, measurements, construction details, and finishing techniques.
- Digital Integration: In virtual fashion design, tech packs are often integrated with the 3D model, providing a comprehensive overview of the garment.
5.2 Virtual Prototyping
Before moving to physical production, designers can create virtual prototypes to test the design and make final adjustments.
- Fit Testing: Virtual prototypes allow for fit testing on digital models, ensuring that the garment meets the desired specifications.
- Material Testing: Designers can also test different materials and finishes virtually, reducing the need for physical samples.
Conclusion
The behind-the-scenes process of virtual fashion design is a complex and creative journey that combines traditional design principles with cutting-edge technology. For fashion designers and buyers, understanding this process is essential for staying competitive in an industry that increasingly values efficiency, sustainability, and innovation. By embracing virtual fashion design, you can unlock new possibilities in creativity, collaboration, and production, paving the way for the future of fashion.